Cord Blood CD34+ Stem/Progenitor Cells, Pooled Donors, Frozen
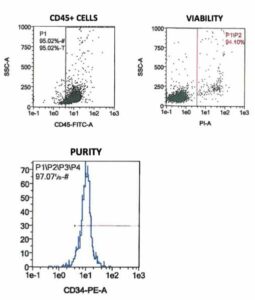
Human cord blood CD34+ stem and progenitor cells are positively selected using immunomagnetic anti-CD34 (clone QBEND10) microbeads from the mononuclear cell fraction. Pooled CD34+ cells are from two or more donors and are available in larger lots. Isolated cells are characterized by flow cytometry prior to cryopreservation to ensure a highly pure and viable cell population.
Cells were obtained using Institutional Review Board (IRB) approved consent forms and protocols.
Since our founding in 2010, CGT Global has pursued our mission to transform healthcare as we accelerate cell and gene therapy research and clinical trials, streamline the commercialization of new treatments, and map the last mile to patient access to these life-changing remedies. By innovating each stage in the cycle; development, commercialization, and delivery, we reduce the overall cost of the care and multiply access points so that millions can receive cutting edge, life-saving gene and cell therapies.

Description
CD34 is a glycosylated transmembrane protein and represents a well-established marker for human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in peripheral blood, bone marrow, and cord blood. CD34+ cells are self-renewing, multipotent stem cells that give rise to all blood cells of the immune system through a process called hematopoiesis. As hematopoietic stem cells progress through hematopoiesis they generate the myeloid (monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, megakaryocytes, dendritic cells, erythrocytes) and lymphoid (T cells, B cells, NK cells) lineages. The highly specialized cells that arise from hematopoietic stem cells work collaboratively in defending the body against infection and disease.
Additional information
| Anticoagulant | |
|---|---|
| Format | |
| Grade | |
| Species | |
| Cell and Tissue Source | |
| Disease State | |
| Donor Attributes |
Product Information Sheet
Cord Blood CD34+ Pooled Donors
Material Safety Data Sheet
Cord Blood CD34+ Stem Cells, Pooled Donors – Frozen
Publications
- Sugimura et al. (2019) Angiocrine Factors from HUVECs Amplify Erythroid Cells. bioRxiv 837823; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/837823. Article